46 KiB
Отчет по теме 4
Цель темы: получение навыков использования встроенных функций языка Python.
Терехов Фёдор Валерьевич, А-01-23
1. Стандартные функции. Находятся в модуле builtins, который становится доступным без импорта при запуске среды IDLE.
1.1. Функция round – округление числа с заданной точностью.
help(round)
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function round in module builtins:
round(number, ndigits=None)
Round a number to a given precision in decimal digits.
The return value is an integer if ndigits is omitted or None. Otherwise
the return value has the same type as the number. ndigits may be negative.
print(round(123.456,1))
print(round(123.456,0))
print('\n')
print(type(round(123.456,1)))
print(type(round(123.456,0)))
print('\n')
print(round(123.456))
print(type(round(123.456)))
print('\n')
Ответ программы:
123.5
123.0
<class 'float'>
<class 'float'>
123
<class 'int'>
1.2. Функция range – создание последовательности целых чисел с заданным шагом или, по умолчанию, с шагом 1.
Аргументами функции являются границы диапазона значений и шаг. При этом правая граница в создаваемую последовательность включена не будет (так же, как это было в «срезах» индексов объектов-последовательностей).
Аргументами функции являются границы диапазона значений и шаг. При этом правая граница в создаваемую последовательность включена не будет (так же, как это было в «срезах» индексов объектов-последовательностей).
Чтобы увидеть получившуюся последовательность чисел, его надо преобразовать, например, в список.
gg=range(76,123,9)
print(list(gg),'\n')
print(list(range(23)))
Ответ программы:
[76, 85, 94, 103, 112, 121]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22]
Если написать например range(23), то будет последовательность от нуля до 23 (не включительно) с шагом 1.
1.3. Функция zip – создание общего объекта, элементами которого являются кортежи, составленные из элементов двух или более объектов-последовательностей (zip – застежка-«молния»).
Длина результирующего объекта равна длине самого короткого объекта из двух аргументов функции.
qq=['Terekhov','Zhalnin', 'Petrov']
ff=zip(qq,gg)
print(tuple(ff))
Ответ программы:
(('Terekhov', 76), ('Zhalnin', 85), ('Petrov', 94))
В получившемся кортеже 3 элемента-кортежа. То есть столько, сколько в наименьшем списке среди двух (qq, gg).
К объекту ff обращаться с указанием индекса.
print(ff[1][0])
Ответ программы:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/user/Desktop/VUZ/3CURSE/POAS_labs/python-labs/TEMA4/task1.py", line 20, in <module>
print(ff[1][0])
~~^^^
TypeError: 'zip' object is not subscriptable
1.4. Функция eval – вычисление значения выражения, корректно записанного на языке Python и представленного в виде символьной строки.
fff=float(input('коэффициент усиления='))
dan=eval('5*fff-156')
print(dan)
Ответ программы:
коэффициент усиления=10
-106.0
1.5. Функция exec – чтение и выполнение объекта-аргумента функции.
exec(input('введите инструкции:'))
print(dir())
Ответ программы:
введите инструкции:perem=-123.456;gg=round(abs(perem)+98,3)
['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'dan', 'ff', 'fff', 'gg', 'perem', 'qq']
Функции eval() и exec() нужно использовать с осторожностью, так как они затрудняют чтение и понимание программ.
1.6. Функция abs - модуль (абсолютное значение).
print(abs(-7), abs(3.5))
Ответ программы:
7 3.5
1.7. Функции min() и max() - минимальное и максимальное значение.
Что принимают:
-
Любой итерируемый объект: строка (максимум по UNICODE-коду), кортеж, множество, диапазон, словарь (сравниваются ключи), и т.д.
-
Либо несколько позиционных аргументов: max(3, 7, 2).
print(max(1,2,3,4,5))
print(min(1,2,3,4,5))
Ответ программы:
5
1
1.8. Функция pow() - возведение в степень.
print(pow(2,3))
print(pow(2,3,5)) # 2**3 = 8, затем 8 % 5 = 3.
Ответ программы:
8
3
1.9. Функция sum() - сумма элементов итерируемого объекта.
Не работает со строками.
print(sum([1,2,3,4,5]))
print(sum((1,2,3,4,5)))
print(sum({1,2,3,4,5}))
Ответ программы:
15
15
15
1.10. Функция divmod() — (целая часть, остаток).
print(divmod(29, 5))
Ответ программы:
(5, 4)
1.11. Функция len() - длина.
print(len([1,2,3,4,5]), len("привет"))
Ответ программы:
5 6
1.12. Функция map(func, iterable, ...) применяет функцию func к каждому элементу(ам) и возвращает итератор результатов.
vals = [3, -8, 5, 0, 12, -1]
r = list(map(abs, vals))
print(r)
Ответ программы:
[3, 8, 5, 0, 12, 1]
2. Функции из стандартного модуля math – совокупность разнообразных математических функций.
Загружается модуль с помощью инструкции import math.
import math
print(dir(math))
Ответ программы:
['__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'acos', 'acosh', 'asin', 'asinh', 'atan', 'atan2', 'atanh', 'cbrt', 'ceil', 'comb', 'copysign', 'cos', 'cosh', 'degrees', 'dist', 'e', 'erf', 'erfc', 'exp', 'exp2', 'expm1', 'fabs', 'factorial', 'floor', 'fmod', 'frexp', 'fsum', 'gamma', 'gcd', 'hypot', 'inf', 'isclose', 'isfinite', 'isinf', 'isnan', 'isqrt', 'lcm', 'ldexp', 'lgamma', 'log', 'log10', 'log1p', 'log2', 'modf', 'nan', 'nextafter', 'perm', 'pi', 'pow', 'prod', 'radians', 'remainder', 'sin', 'sinh', 'sqrt', 'tan', 'tanh', 'tau', 'trunc', 'ulp']
2.1. Функция расчета факториала factorial.
help(math.factorial)
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function factorial in module math:
factorial(n, /)
Find n!.
Raise a ValueError if x is negative or non-integral.
print(math.factorial(5))
Ответ программы:
120
2.2. Функция sin.
print(help(math.sin))
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function sin in module math:
sin(x, /)
Return the sine of x (measured in radians).
print(math.sin(math.pi/2))
Ответ программы:
1.0
2.3. Функция acos.
print(help(math.acos))
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function acos in module math:
acos(x, /)
Return the arc cosine (measured in radians) of x.
The result is between 0 and pi.
print(math.acos(1))
Ответ программы:
0.0
2.4. Функция degrees.
print(help(math.degrees))
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function degrees in module math:
degrees(x, /)
Convert angle x from radians to degrees.
print(math.degrees(math.pi))
Ответ программы:
180.0
2.5. Функция radians.
print(help(math.radians))
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function radians in module math:
radians(x, /)
Convert angle x from degrees to radians.
print(math.radians(180))
Ответ программы:
3.141592653589793
2.6. Функция exp.
print(help(math.exp))
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function exp in module math:
exp(x, /)
Return e raised to the power of x.
print(math.exp(2))
Ответ программы:
7.38905609893065
2.7. Функция log.
print(help(math.log))
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function log in module math:
log(...)
log(x, [base=math.e])
Return the logarithm of x to the given base.
If the base not specified, returns the natural logarithm (base e) of x.
print(math.log(math.e))
print(math.log(4,2))
Ответ программы:
1.0
2.0
2.8. Функция log10.
print(help(math.log10))
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function log10 in module math:
log10(x, /)
Return the base 10 logarithm of x.
print(math.log10(100))
Ответ программы:
2.0
2.9. Функция sqrt.
print(help(math.sqrt))
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function sqrt in module math:
sqrt(x, /)
Return the square root of x.
print(math.sqrt(100))
Ответ программы:
10.0
2.10. Функция ceil.
print(help(math.ceil))
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function ceil in module math:
ceil(x, /)
Return the ceiling of x as an Integral.
This is the smallest integer >= x.
print(math.ceil(100.2))
Ответ программы:
101
2.11. Функция floor.
print(help(math.floor))
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function floor in module math:
floor(x, /)
Return the floor of x as an Integral.
This is the largest integer <= x.
print(math.floor(100.2))
Ответ программы:
100
2.12. Число pi.
print(help(math.pi)) #Выведет справку по типу float
print(math.pi)
print(type(math.pi))
Ответ программы:
3.141592653589793
<class 'float'>
2.13. Вычисление sin(2π/7+e^0.23).
print(math.sin(2*math.pi/7+math.exp(0.23)))
Ответ программы:
0.8334902641414562
3. Функции из модуля cmath – совокупность функций для работы с комплексными числами.
Импорт модуля.
import cmath
print(dir(cmath))
Ответ программы:
['__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'acos', 'acosh', 'asin', 'asinh', 'atan', 'atanh', 'cos', 'cosh', 'e', 'exp', 'inf', 'infj', 'isclose', 'isfinite', 'isinf', 'isnan', 'log', 'log10', 'nan', 'nanj', 'phase', 'pi', 'polar', 'rect', 'sin', 'sinh', 'sqrt', 'tan', 'tanh', 'tau']
3.1. Функция cmath.sqrt().
print(help(cmath.sqrt))
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function sqrt in module cmath:
sqrt(z, /)
Return the square root of z.
print(cmath.sqrt(1.2-0.5j))
Ответ программы:
(1.118033988749895-0.22360679774997896j)
3.2. Функция cmath.phase().
print(help(cmath.phase))
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function phase in module cmath:
phase(z, /)
Return argument, also known as the phase angle, of a complex.
print(cmath.phase(1-0.5j))
Ответ программы:
-0.4636476090008061
4. Стандартный модуль random – совокупность функций для выполнения операций с псевдослучайными числами и выборками.
Импорт модуля.
import random
print(dir(random))
Ответ программы:
['BPF', 'LOG4', 'NV_MAGICCONST', 'RECIP_BPF', 'Random', 'SG_MAGICCONST', 'SystemRandom', 'TWOPI', '_ONE', '_Sequence', '_Set', '__all__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', '_accumulate', '_acos', '_bisect', '_ceil', '_cos', '_e', '_exp', '_floor', '_index', '_inst', '_isfinite', '_log', '_os', '_pi', '_random', '_repeat', '_sha512', '_sin', '_sqrt', '_test', '_test_generator', '_urandom', '_warn', 'betavariate', 'choice', 'choices', 'expovariate', 'gammavariate', 'gauss', 'getrandbits', 'getstate', 'lognormvariate', 'normalvariate', 'paretovariate', 'randbytes', 'randint', 'random', 'randrange', 'sample', 'seed', 'setstate', 'shuffle', 'triangular', 'uniform', 'vonmisesvariate', 'weibullvariate']
4.1. Функция seed - задаёт случайное начальное состояние для псевдослучайных чисел.
help(random.seed)
Ответ программы:
Help on method seed in module random:
seed(a=None, version=2) method of random.Random instance
Initialize internal state from a seed.
The only supported seed types are None, int, float,
str, bytes, and bytearray.
None or no argument seeds from current time or from an operating
system specific randomness source if available.
If *a* is an int, all bits are used.
For version 2 (the default), all of the bits are used if *a* is a str,
bytes, or bytearray. For version 1 (provided for reproducing random
sequences from older versions of Python), the algorithm for str and
bytes generates a narrower range of seeds.
4.2. Функция random - равномерно распределенное случайное число.
help(random.random)
Help on built-in function random:
random() method of random.Random instance
random() -> x in the interval [0, 1).
random.seed(1)
print(random.random())
Ответ программы:
0.13436424411240122
4.3. Функция uniform - равномерно распределенное случайное число.
help(random.uniform)
Help on method uniform in module random:
uniform(a, b) method of random.Random instance
Get a random number in the range [a, b) or [a, b] depending on rounding.
random.seed(1)
print(random.uniform(1,10))
Ответ программы:
2.209278197011611
4.4. Функция randint - случайные целые числа.
help(random.randint)
Help on method randint in module random:
randint(a, b) method of random.Random instance
Return random integer in range [a, b], including both end points.
random.seed(1)
print(random.randint(1,10))
Ответ программы:
3
4.5. Функция gauss - нормально распределенное случайное число.
help(random.gauss)
Help on method gauss in module random:
gauss(mu=0.0, sigma=1.0) method of random.Random instance
Gaussian distribution.
mu is the mean, and sigma is the standard deviation. This is
slightly faster than the normalvariate() function.
Not thread-safe without a lock around calls.
random.seed(1)
print(random.randint(1,10))
Ответ программы:
1.2881847531554629
4.6. Функция choice - случайный выбор из совокупности.
help(random.choice)
Help on method choice in module random:
choice(seq) method of random.Random instance
Choose a random element from a non-empty sequence.
print(random.choice(['a','b','c']))
Ответ программы:
c
4.7. Функция shuffle - случайная перестановка элементов списка.
help(random.shuffle)
Help on method shuffle in module random:
shuffle(x) method of random.Random instance
Shuffle list x in place, and return None.
lst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
random.shuffle(lst)
print(lst)
Ответ программы:
[3, 4, 5, 1, 2]
4.8. Функция sample - случайный выбор подмножества элементов.
help(random.sample)
Help on method sample in module random:
sample(population, k, *, counts=None) method of random.Random instance
Chooses k unique random elements from a population sequence.
Returns a new list containing elements from the population while
leaving the original population unchanged. The resulting list is
in selection order so that all sub-slices will also be valid random
samples. This allows raffle winners (the sample) to be partitioned
into grand prize and second place winners (the subslices).
Members of the population need not be hashable or unique. If the
population contains repeats, then each occurrence is a possible
selection in the sample.
Repeated elements can be specified one at a time or with the optional
counts parameter. For example:
sample(['red', 'blue'], counts=[4, 2], k=5)
is equivalent to:
sample(['red', 'red', 'red', 'red', 'blue', 'blue'], k=5)
To choose a sample from a range of integers, use range() for the
population argument. This is especially fast and space efficient
for sampling from a large population:
sample(range(10000000), 60)
print(random.sample(range(10), 3))
Ответ программы:
[2, 3, 1]
4.9. Функция betavariate - случайное число с бета-распределением.
help(random.betavariate)
Help on method betavariate in module random:
betavariate(alpha, beta) method of random.Random instance
Beta distribution.
Conditions on the parameters are alpha > 0 and beta > 0.
Returned values range between 0 and 1.
print(random.betavariate(2.0, 5.0))
Ответ программы:
0.49241413359692204
4.10. Функция gammavariate - случайное число с гамма-распределением.
help(random.gammavariate)
Help on method gammavariate in module random:
gammavariate(alpha, beta) method of random.Random instance
Gamma distribution. Not the gamma function!
Conditions on the parameters are alpha > 0 and beta > 0.
The probability distribution function is:
x ** (alpha - 1) * math.exp(-x / beta)
pdf(x) = --------------------------------------
math.gamma(alpha) * beta ** alpha
print(random.gammavariate(2.0, 5.0))
Ответ программы:
9.82488235839505
4.11. Список с 4 случайными значениями, подчиняющимися, соответственно, равномерному, нормальному, бета и гамма – распределениям.
val_uniform = random.uniform(-5, 5) # равномерное на [-5, 5]
val_normal = random.gauss(0, 2) # нормальное N(μ=0, σ=2)
val_beta = random.betavariate(2.0, 5.0) # бета(α=2, β=5), в [0,1]
val_gamma = random.gammavariate(3.0, 2.0) # гамма(k=3, θ=2)
values = [val_uniform, val_normal, val_beta, val_gamma]
print(values)
Ответ программы:
[-1.4734596483177196, -0.8409958083326963, 0.6338143053774301, 3.956751590579974]
5. Функции из модуля time – работа с календарем и со временем.
Импорт модуля.
import time
print(dir(time))
Ответ программы:
['CLOCK_BOOTTIME', 'CLOCK_MONOTONIC', 'CLOCK_MONOTONIC_RAW', 'CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID', 'CLOCK_REALTIME', 'CLOCK_TAI', 'CLOCK_THREAD_CPUTIME_ID', '_STRUCT_TM_ITEMS', '__doc__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'altzone', 'asctime', 'clock_getres', 'clock_gettime', 'clock_gettime_ns', 'clock_settime', 'clock_settime_ns', 'ctime', 'daylight', 'get_clock_info', 'gmtime', 'localtime', 'mktime', 'monotonic', 'monotonic_ns', 'perf_counter', 'perf_counter_ns', 'process_time', 'process_time_ns', 'pthread_getcpuclockid', 'sleep', 'strftime', 'strptime', 'struct_time', 'thread_time', 'thread_time_ns', 'time', 'time_ns', 'timezone', 'tzname', 'tzset']
5.1. Функция time - возвращает время в секундах, прошедшее с начала эпохи, за которое обычно принимается 1.01.1970г.
c1=time.time()
c2=time.time()-c1
print(c2)
Ответ программы:
7.152557373046875e-07
5.2. Функция gmtime - возвращает объект класса struct_time, содержащий полную информацию о текущем времени: год (tm_year), месяц (tm_mon), день tm_mday),….
dat=time.gmtime()
print(dat)
Ответ программы:
time.struct_time(tm_year=2025, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=3, tm_hour=11, tm_min=14, tm_sec=34, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=276, tm_isdst=0)
Эта функция возвращает, так называемое, «Всемирное координированное время» (UTC). Московское время MSK опережает UTC на 3 часа
dat=time.gmtime()
print(dat.tm_mon)
Ответ программы:
10
5.3. Функция localtime - возвращает объект класса struct_time, содержащий полную информацию о текущем местном времени: год (tm_year), месяц (tm_mon), день tm_mday),….
help(time.localtime)
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function localtime in module time:
localtime(...)
localtime([seconds]) -> (tm_year,tm_mon,tm_mday,tm_hour,tm_min,
tm_sec,tm_wday,tm_yday,tm_isdst)
Convert seconds since the Epoch to a time tuple expressing local time.
When 'seconds' is not passed in, convert the current time instead.
dat=time.localtime()
print(dat)
Ответ программы:
time.struct_time(tm_year=2025, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=3, tm_hour=14, tm_min=16, tm_sec=52, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=276, tm_isdst=0)
Обратное преобразование из секунд в местное время осуществляется той же функцией localtime():
c1=time.time()
print(time.localtime(c1))
Ответ программы:
time.struct_time(tm_year=2025, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=3, tm_hour=14, tm_min=32, tm_sec=46, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=276, tm_isdst=0)
5.4. Функция asctime - преобразование представления времени из кортежа в строку.
help(time.asctime)
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function asctime in module time:
asctime(...)
asctime([tuple]) -> string
Convert a time tuple to a string, e.g. 'Sat Jun 06 16:26:11 1998'.
When the time tuple is not present, current time as returned by localtime()
is used.
dat=time.asctime()
print(dat)
Ответ программы:
Fri Oct 3 14:21:36 2025
5.5. Функция ctime - преобразование времени в секундах, прошедшего с начала эпохи, в строку.
help(time.ctime)
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function ctime in module time:
ctime(...)
ctime(seconds) -> string
Convert a time in seconds since the Epoch to a string in local time.
This is equivalent to asctime(localtime(seconds)). When the time tuple is
not present, current time as returned by localtime() is used.
dat=time.ctime(10**10)
print(dat)
Ответ программы:
Sat Nov 20 20:46:40 2286
5.6. Функция sleep - прерывание работы программы на заданное время.
help(time.sleep)
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function sleep in module time:
sleep(...)
sleep(seconds)
Delay execution for a given number of seconds. The argument may be
a floating point number for subsecond precision.
time.sleep(3)
Ответ программы:
Терминал прервал свою работу на 3 секунды
5.7. Функция mktime - преобразование времени из типа кортежа или struct_time в число секунд с начала эпохи.
help(time.mktime)
Ответ программы:
Help on built-in function mktime in module time:
mktime(...)
mktime(tuple) -> floating point number
Convert a time tuple in local time to seconds since the Epoch.
Note that mktime(gmtime(0)) will not generally return zero for most
time zones; instead the returned value will either be equal to that
of the timezone or altzone attributes on the time module.
dat=time.localtime()
print(dat)
print(time.mktime(dat))
Ответ программы:
time.struct_time(tm_year=2025, tm_mon=10, tm_mday=3, tm_hour=14, tm_min=31, tm_sec=27, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=276, tm_isdst=0)
1759491087.0
6. Графические функции. pylab.
Импорт модуля.
import pylab
print(dir(pylab))
Ответ программы:
['AbstractContextManager', 'Annotation', 'Arrow', 'Artist', 'AutoLocator', 'AxLine', 'Axes', 'BackendFilter', 'BitGenerator', 'Button', 'Circle', 'Colorizer', 'ColorizingArtist', 'Colormap', 'DAILY', 'DateFormatter', 'DateLocator', 'DayLocator', 'Enum', 'ExitStack', 'FR', 'False_', 'Figure', 'FigureBase', 'FigureCanvasBase', 'FigureManagerBase', 'FixedFormatter', 'FixedLocator', 'FormatStrFormatter', 'Formatter', 'FuncFormatter', 'Generator', 'GridSpec', 'HOURLY', 'HourLocator', 'IndexLocator', 'LinAlgError', 'Line2D', 'LinearLocator', 'Locator', 'LogFormatter', 'LogFormatterExponent', 'LogFormatterMathtext', 'LogLocator', 'MINUTELY', 'MO', 'MONTHLY', 'MT19937', 'MaxNLocator', 'MinuteLocator', 'MonthLocator', 'MouseButton', 'MultipleLocator', 'Normalize', 'NullFormatter', 'NullLocator', 'PCG64', 'PCG64DXSM', 'Philox', 'PolarAxes', 'Polygon', 'RRuleLocator', 'RandomState', 'Rectangle', 'SA', 'SECONDLY', 'SFC64', 'SU', 'ScalarFormatter', 'ScalarType', 'SecondLocator', 'SeedSequence', 'Slider', 'Subplot', 'SubplotSpec', 'TH', 'TU', 'TYPE_CHECKING', 'Text', 'TickHelper', 'True_', 'WE', 'WEEKLY', 'WeekdayLocator', 'Widget', 'YEARLY', 'YearLocator', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'abs', 'absolute', 'acorr', 'acos', 'acosh', 'add', 'all', 'allclose', 'amax', 'amin', 'angle', 'angle_spectrum', 'annotate', 'annotations', 'any', 'append', 'apply_along_axis', 'apply_over_axes', 'arange', 'arccos', 'arccosh', 'arcsin', 'arcsinh', 'arctan', 'arctan2', 'arctanh', 'argmax', 'argmin', 'argpartition', 'argsort', 'argwhere', 'around', 'array', 'array2string', 'array_equal', 'array_equiv', 'array_repr', 'array_split', 'array_str', 'arrow', 'asanyarray', 'asarray', 'asarray_chkfinite', 'ascontiguousarray', 'asfortranarray', 'asin', 'asinh', 'asmatrix', 'astype', 'atan', 'atan2', 'atanh', 'atleast_1d', 'atleast_2d', 'atleast_3d', 'autoscale', 'autumn', 'available_backends', 'average', 'axes', 'axhline', 'axhspan', 'axis', 'axline', 'axvline', 'axvspan', 'backend_registry', 'bar', 'bar_label', 'barbs', 'barh', 'bartlett', 'base_repr', 'beta', 'binary_repr', 'bincount', 'binomial', 'bitwise_and', 'bitwise_count', 'bitwise_invert', 'bitwise_left_shift', 'bitwise_not', 'bitwise_or', 'bitwise_right_shift', 'bitwise_xor', 'blackman', 'block', 'bmat', 'bone', 'bool', 'bool_', 'box', 'boxplot', 'broadcast', 'broadcast_arrays', 'broadcast_shapes', 'broadcast_to', 'broken_barh', 'busday_count', 'busday_offset', 'busdaycalendar', 'byte', 'bytes', 'bytes_', 'c_', 'can_cast', 'cast', 'cbook', 'cbrt', 'cdouble', 'ceil', 'char', 'character', 'chisquare', 'choice', 'cholesky', 'choose', 'cla', 'clabel', 'clf', 'clim', 'clip', 'clongdouble', 'close', 'cm', 'cohere', 'color_sequences', 'colorbar', 'colormaps', 'column_stack', 'common_type', 'complex128', 'complex256', 'complex64', 'complexfloating', 'compress', 'concat', 'concatenate', 'cond', 'conj', 'conjugate', 'connect', 'contour', 'contourf', 'convolve', 'cool', 'copper', 'copy', 'copysign', 'copyto', 'core', 'corrcoef', 'correlate', 'cos', 'cosh', 'count_nonzero', 'cov', 'cross', 'csd', 'csingle', 'ctypeslib', 'cumprod', 'cumsum', 'cumulative_prod', 'cumulative_sum', 'cycler', 'date2num', 'datestr2num', 'datetime', 'datetime64', 'datetime_as_string', 'datetime_data', 'default_rng', 'deg2rad', 'degrees', 'delaxes', 'delete', 'det', 'detrend', 'detrend_linear', 'detrend_mean', 'detrend_none', 'diag', 'diag_indices', 'diag_indices_from', 'diagflat', 'diagonal', 'diff', 'digitize', 'dirichlet', 'disconnect', 'divide', 'divmod', 'dot', 'double', 'drange', 'draw', 'draw_all', 'draw_if_interactive', 'dsplit', 'dstack', 'dtype', 'dtypes', 'e', 'ecdf', 'ediff1d', 'eig', 'eigh', 'eigvals', 'eigvalsh', 'einsum', 'einsum_path', 'emath', 'empty', 'empty_like', 'equal', 'errorbar', 'errstate', 'euler_gamma', 'eventplot', 'exceptions', 'exp', 'exp2', 'expand_dims', 'expm1', 'exponential', 'extract', 'eye', 'f', 'f2py', 'fabs', 'fft', 'fft2', 'fftfreq', 'fftn', 'fftshift', 'figaspect', 'figimage', 'figlegend', 'fignum_exists', 'figtext', 'figure', 'fill', 'fill_between', 'fill_betweenx', 'fill_diagonal', 'findobj', 'finfo', 'fix', 'flag', 'flatiter', 'flatnonzero', 'flatten', 'flexible', 'flip', 'fliplr', 'flipud', 'float128', 'float16', 'float32', 'float64', 'float_power', 'floating', 'floor', 'floor_divide', 'fmax', 'fmin', 'fmod', 'format_float_positional', 'format_float_scientific', 'frexp', 'from_dlpack', 'frombuffer', 'fromfile', 'fromfunction', 'fromiter', 'frompyfunc', 'fromregex', 'fromstring', 'full', 'full_like', 'functools', 'gamma', 'gca', 'gcd', 'gcf', 'gci', 'generic', 'genfromtxt', 'geometric', 'geomspace', 'get', 'get_backend', 'get_cmap', 'get_current_fig_manager', 'get_figlabels', 'get_fignums', 'get_include', 'get_plot_commands', 'get_printoptions', 'get_scale_names', 'get_state', 'getbufsize', 'geterr', 'geterrcall', 'getp', 'ginput', 'gradient', 'gray', 'greater', 'greater_equal', 'grid', 'gumbel', 'half', 'hamming', 'hanning', 'heaviside', 'hexbin', 'hfft', 'hist', 'hist2d', 'histogram', 'histogram2d', 'histogram_bin_edges', 'histogramdd', 'hlines', 'hot', 'hsplit', 'hstack', 'hsv', 'hypergeometric', 'hypot', 'i0', 'identity', 'ifft', 'ifft2', 'ifftn', 'ifftshift', 'ihfft', 'iinfo', 'imag', 'importlib', 'imread', 'imsave', 'imshow', 'in1d', 'index_exp', 'indices', 'inexact', 'inf', 'inferno', 'info', 'inner', 'insert', 'inspect', 'install_repl_displayhook', 'int16', 'int32', 'int64', 'int8', 'int_', 'intc', 'integer', 'interactive', 'interp', 'intersect1d', 'intp', 'inv', 'invert', 'ioff', 'ion', 'irfft', 'irfft2', 'irfftn', 'is_busday', 'isclose', 'iscomplex', 'iscomplexobj', 'isdtype', 'isfinite', 'isfortran', 'isin', 'isinf', 'isinteractive', 'isnan', 'isnat', 'isneginf', 'isposinf', 'isreal', 'isrealobj', 'isscalar', 'issubdtype', 'iterable', 'ix_', 'jet', 'kaiser', 'kron', 'laplace', 'lcm', 'ldexp', 'left_shift', 'legend', 'less', 'less_equal', 'lexsort', 'lib', 'linalg', 'linspace', 'little_endian', 'load', 'loadtxt', 'locator_params', 'log', 'log10', 'log1p', 'log2', 'logaddexp', 'logaddexp2', 'logging', 'logical_and', 'logical_not', 'logical_or', 'logical_xor', 'logistic', 'loglog', 'lognormal', 'logseries', 'logspace', 'long', 'longdouble', 'longlong', 'lstsq', 'ma', 'magma', 'magnitude_spectrum', 'margins', 'mask_indices', 'matmul', 'matplotlib', 'matrix', 'matrix_norm', 'matrix_power', 'matrix_rank', 'matrix_transpose', 'matshow', 'matvec', 'max', 'maximum', 'may_share_memory', 'mean', 'median', 'memmap', 'meshgrid', 'mgrid', 'min', 'min_scalar_type', 'minimum', 'minorticks_off', 'minorticks_on', 'mintypecode', 'mlab', 'mod', 'modf', 'moveaxis', 'mpl', 'multi_dot', 'multinomial', 'multiply', 'multivariate_normal', 'nan', 'nan_to_num', 'nanargmax', 'nanargmin', 'nancumprod', 'nancumsum', 'nanmax', 'nanmean', 'nanmedian', 'nanmin', 'nanpercentile', 'nanprod', 'nanquantile', 'nanstd', 'nansum', 'nanvar', 'ndarray', 'ndenumerate', 'ndim', 'ndindex', 'nditer', 'negative', 'negative_binomial', 'nested_iters', 'new_figure_manager', 'newaxis', 'nextafter', 'nipy_spectral', 'noncentral_chisquare', 'noncentral_f', 'nonzero', 'norm', 'normal', 'not_equal', 'np', 'num2date', 'number', 'object_', 'ogrid', 'ones', 'ones_like', 'outer', 'overload', 'packbits', 'pad', 'pareto', 'partition', 'pause', 'pcolor', 'pcolormesh', 'percentile', 'permutation', 'permute_dims', 'phase_spectrum', 'pi', 'pie', 'piecewise', 'pink', 'pinv', 'place', 'plasma', 'plot', 'plot_date', 'plt', 'poisson', 'polar', 'poly', 'poly1d', 'polyadd', 'polyder', 'polydiv', 'polyfit', 'polyint', 'polymul', 'polynomial', 'polysub', 'polyval', 'positive', 'pow', 'power', 'printoptions', 'prism', 'prod', 'promote_types', 'psd', 'ptp', 'put', 'put_along_axis', 'putmask', 'qr', 'quantile', 'quiver', 'quiverkey', 'r_', 'rad2deg', 'radians', 'rand', 'randint', 'randn', 'random', 'random_integers', 'random_sample', 'ranf', 'ravel', 'ravel_multi_index', 'rayleigh', 'rc', 'rcParams', 'rcParamsDefault', 'rcParamsOrig', 'rc_context', 'rcdefaults', 'rcsetup', 'real', 'real_if_close', 'rec', 'recarray', 'reciprocal', 'record', 'relativedelta', 'remainder', 'repeat', 'requested_backend', 'require', 'reshape', 'resize', 'result_type', 'rfft', 'rfft2', 'rfftfreq', 'rfftn', 'rgrids', 'right_shift', 'rint', 'roll', 'rollaxis', 'roots', 'rot90', 'round', 'row_stack', 'rrule', 's_', 'sample', 'save', 'savefig', 'savetxt', 'savez', 'savez_compressed', 'sca', 'scatter', 'sci', 'sctypeDict', 'searchsorted', 'seed', 'select', 'semilogx', 'semilogy', 'set_cmap', 'set_loglevel', 'set_printoptions', 'set_state', 'setbufsize', 'setdiff1d', 'seterr', 'seterrcall', 'setp', 'setxor1d', 'shape', 'shares_memory', 'short', 'show', 'show_config', 'show_runtime', 'shuffle', 'sign', 'signbit', 'signedinteger', 'silent_list', 'sin', 'sinc', 'single', 'sinh', 'size', 'slogdet', 'solve', 'sort', 'sort_complex', 'spacing', 'specgram', 'split', 'spring', 'spy', 'sqrt', 'square', 'squeeze', 'stack', 'stackplot', 'stairs', 'standard_cauchy', 'standard_exponential', 'standard_gamma', 'standard_normal', 'standard_t', 'std', 'stem', 'step', 'str_', 'streamplot', 'strings', 'style', 'subplot', 'subplot2grid', 'subplot_mosaic', 'subplot_tool', 'subplots', 'subplots_adjust', 'subtract', 'sum', 'summer', 'suptitle', 'svd', 'svdvals', 'swapaxes', 'switch_backend', 'sys', 'table', 'take', 'take_along_axis', 'tan', 'tanh', 'tensordot', 'tensorinv', 'tensorsolve', 'test', 'testing', 'text', 'thetagrids', 'threading', 'tick_params', 'ticklabel_format', 'tight_layout', 'tile', 'time', 'timedelta64', 'title', 'trace', 'transpose', 'trapezoid', 'trapz', 'tri', 'triangular', 'tricontour', 'tricontourf', 'tril', 'tril_indices', 'tril_indices_from', 'trim_zeros', 'tripcolor', 'triplot', 'triu', 'triu_indices', 'triu_indices_from', 'true_divide', 'trunc', 'twinx', 'twiny', 'typecodes', 'typename', 'typing', 'ubyte', 'ufunc', 'uint', 'uint16', 'uint32', 'uint64', 'uint8', 'uintc', 'uintp', 'ulong', 'ulonglong', 'uniform', 'uninstall_repl_displayhook', 'union1d', 'unique', 'unique_all', 'unique_counts', 'unique_inverse', 'unique_values', 'unpackbits', 'unravel_index', 'unsignedinteger', 'unstack', 'unwrap', 'ushort', 'vander', 'var', 'vdot', 'vecdot', 'vecmat', 'vector_norm', 'vectorize', 'violinplot', 'viridis', 'vlines', 'void', 'vonmises', 'vsplit', 'vstack', 'waitforbuttonpress', 'wald', 'weibull', 'where', 'window_hanning', 'window_none', 'winter', 'xcorr', 'xkcd', 'xlabel', 'xlim', 'xscale', 'xticks', 'ylabel', 'ylim', 'yscale', 'yticks', 'zeros', 'zeros_like', 'zipf']
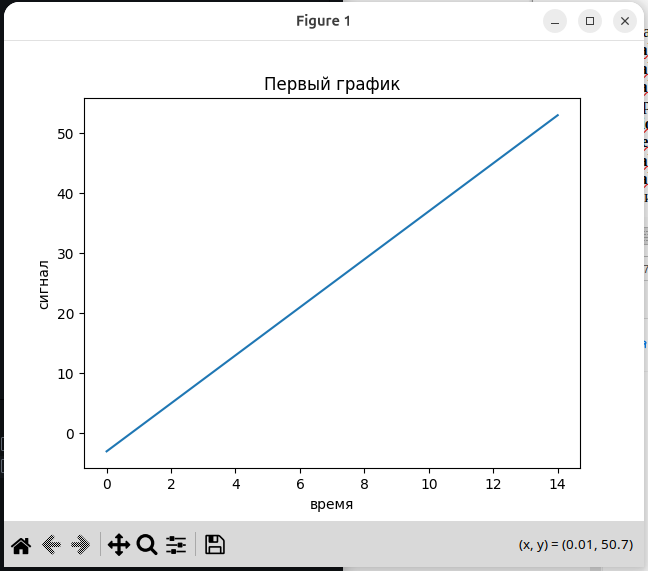
6.1. Функция time - возвращает время в секундах, прошедшее с начала эпохи, за которое обычно принимается 1.01.1970г.
import pylab
x=list(range(-3,55,4))
t=list(range(15))
pylab.plot(t,x) #Создание графика в оперативной памяти
pylab.title('Первый график')
pylab.xlabel('время')
pylab.ylabel('сигнал')
pylab.show() #Отображение графика на экране
Ответ программы:
Сохранение файла:
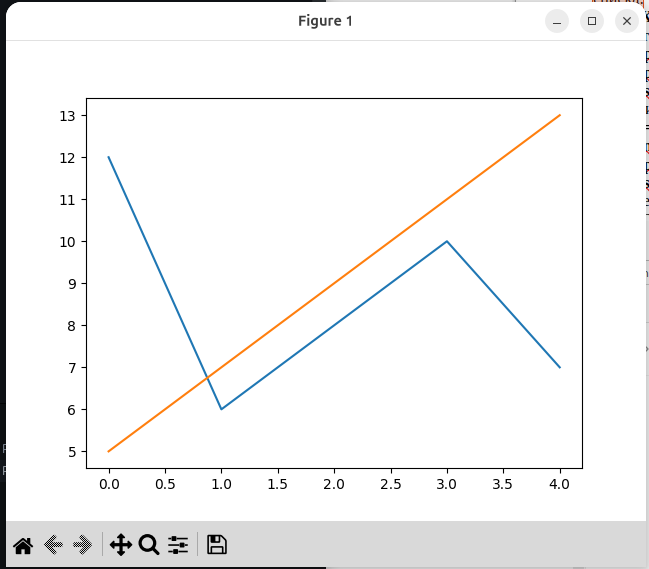
6.2. Способ построения нескольких графиков на одном рисунке.
import pylab
X1=[12,6,8,10,7]
X2=[5,7,9,11,13]
pylab.plot(X1)
pylab.plot(X2)
pylab.show()
Ответ программы:
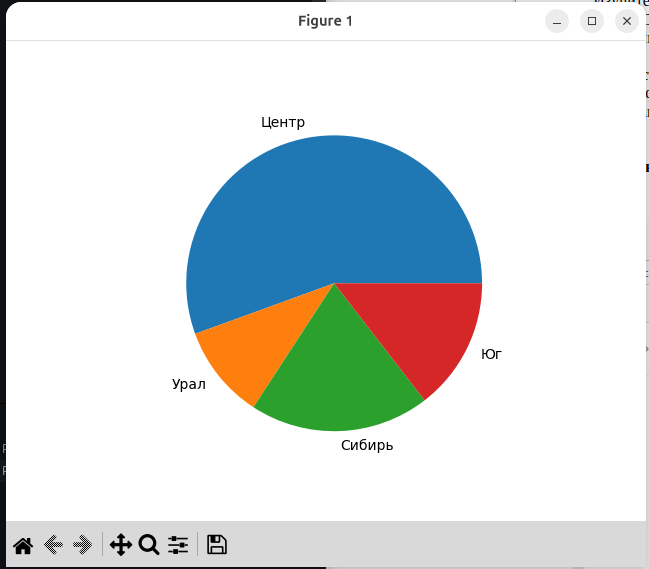
6.3. Построение круговой диаграммы.
import pylab
region=['Центр','Урал','Сибирь','Юг'] #Метки для диаграммы
naselen=[65,12,23,17] # Значения для диаграммы
pylab.pie(naselen,labels=region) #Создание диаграммы в памяти
pylab.show() #Отображение диаграммы
Ответ программы:
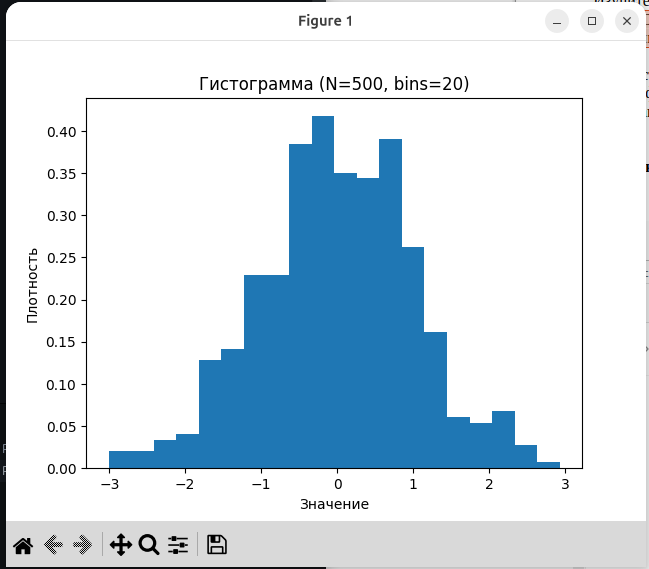
6.4. Построение гистограммы - hist.
import pylab
import random
data = [random.gauss(0, 1) for _ in range(500)]
pylab.figure()
pylab.hist(data, bins=20, density=True)
pylab.title("Гистограмма (N=500, bins=20)")
pylab.xlabel("Значение")
pylab.ylabel("Плотность")
pylab.show()
Ответ программы:
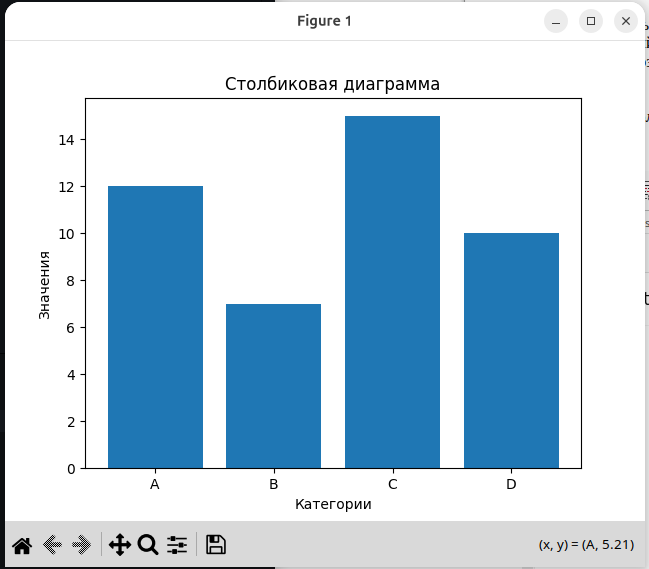
6.5. Построение столбиковой диаграммы - bar.
import pylab
labels = ["A", "B", "C", "D"]
values = [12, 7, 15, 10]
pylab.figure()
pylab.bar(labels, values)
pylab.title("Столбиковая диаграмма")
pylab.xlabel("Категории")
pylab.ylabel("Значения")
pylab.show()
Ответ программы:
7. Модуль statistics.
Импорт модуля.
import statistics
print(dir(statistics))
Ответ программы:
['Counter', 'Decimal', 'Fraction', 'LinearRegression', 'NormalDist', 'StatisticsError', '_SQRT2', '__all__', '__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', '_coerce', '_convert', '_decimal_sqrt_of_frac', '_exact_ratio', '_fail_neg', '_float_sqrt_of_frac', '_integer_sqrt_of_frac_rto', '_isfinite', '_mean_stdev', '_normal_dist_inv_cdf', '_sqrt_bit_width', '_ss', '_sum', 'bisect_left', 'bisect_right', 'correlation', 'covariance', 'defaultdict', 'erf', 'exp', 'fabs', 'fmean', 'fsum', 'geometric_mean', 'groupby', 'harmonic_mean', 'hypot', 'linear_regression', 'log', 'math', 'mean', 'median', 'median_grouped', 'median_high', 'median_low', 'mode', 'mul', 'multimode', 'namedtuple', 'numbers', 'pstdev', 'pvariance', 'quantiles', 'random', 'reduce', 'repeat', 'sqrt', 'stdev', 'sys', 'tau', 'variance']
7.1. Среднее арифметическое - statistics.mean().
import statistics
grades = [85, 90, 78, 92, 88, 76, 95, 85, 80, 82, 91, 85]
print("Список оценок:", grades)
print("Количество студентов:", len(grades))
print()
average_grade = statistics.mean(grades)
print(f"1. Средний балл (mean): {average_grade:.2f}")
Ответ программы:
Список оценок: [85, 90, 78, 92, 88, 76, 95, 85, 80, 82, 91, 85]
Количество студентов: 12
1. Средний балл (mean): 85.58
7.2. Медиана - statistics.median().
import statistics
grades = [85, 90, 78, 92, 88, 76, 95, 85, 80, 82, 91, 85]
print("Список оценок:", grades)
print("Количество студентов:", len(grades))
print()
average_grade = statistics.mean(grades)
print(f"1. Средний балл (mean): {average_grade:.2f}")
median_grade = statistics.median(grades)
print(f"2. Медианный балл (median): {median_grade}")
Ответ программы:
Список оценок: [85, 90, 78, 92, 88, 76, 95, 85, 80, 82, 91, 85]
Количество студентов: 12
1. Средний балл (mean): 85.58
2. Медианный балл (median): 85.0
7.3. Мода - statistics.mode().
import statistics
grades = [85, 90, 78, 92, 88, 76, 95, 85, 80, 82, 91, 85]
print("Список оценок:", grades)
print("Количество студентов:", len(grades))
print()
average_grade = statistics.mean(grades)
print(f"1. Средний балл (mean): {average_grade:.2f}")
median_grade = statistics.median(grades)
print(f"2. Медианный балл (median): {median_grade}")
mode_grade = statistics.mode(grades)
print(f"3. Наиболее частый балл (mode): {mode_grade}")
Ответ программы:
Список оценок: [85, 90, 78, 92, 88, 76, 95, 85, 80, 82, 91, 85]
Количество студентов: 12
1. Средний балл (mean): 85.58
2. Медианный балл (median): 85.0
3. Наиболее частый балл (mode): 85
7.4. Стандартное отклонение - statistics.stdev().
import statistics
grades = [85, 90, 78, 92, 88, 76, 95, 85, 80, 82, 91, 85]
print("Список оценок:", grades)
print("Количество студентов:", len(grades))
print()
average_grade = statistics.mean(grades)
print(f"1. Средний балл (mean): {average_grade:.2f}")
median_grade = statistics.median(grades)
print(f"2. Медианный балл (median): {median_grade}")
mode_grade = statistics.mode(grades)
print(f"3. Наиболее частый балл (mode): {mode_grade}")
stdev_grades = statistics.stdev(grades)
print(f"4. Стандартное отклонение (stdev): {stdev_grades:.2f}")
Ответ программы:
Список оценок: [85, 90, 78, 92, 88, 76, 95, 85, 80, 82, 91, 85]
Количество студентов: 12
1. Средний балл (mean): 85.58
2. Медианный балл (median): 85.0
3. Наиболее частый балл (mode): 85
4. Стандартное отклонение (stdev): 5.87
7.5. Дисперсия - statistics.variance().
import statistics
grades = [85, 90, 78, 92, 88, 76, 95, 85, 80, 82, 91, 85]
print("Список оценок:", grades)
print("Количество студентов:", len(grades))
print()
average_grade = statistics.mean(grades)
print(f"1. Средний балл (mean): {average_grade:.2f}")
median_grade = statistics.median(grades)
print(f"2. Медианный балл (median): {median_grade}")
mode_grade = statistics.mode(grades)
print(f"3. Наиболее частый балл (mode): {mode_grade}")
stdev_grades = statistics.stdev(grades)
print(f"4. Стандартное отклонение (stdev): {stdev_grades:.2f}")
variance_grades = statistics.variance(grades)
print(f"5. Дисперсия (variance): {variance_grades:.2f}")
Ответ программы:
Список оценок: [85, 90, 78, 92, 88, 76, 95, 85, 80, 82, 91, 85]
Количество студентов: 12
1. Средний балл (mean): 85.58
2. Медианный балл (median): 85.0
3. Наиболее частый балл (mode): 85
4. Стандартное отклонение (stdev): 5.87
5. Дисперсия (variance): 34.45